ENCRYPTION

Establish secure connections and password protect your files.
SYMMETRICAL

01
Mcrypt
Mcrypt uses symmetric file encryption by default. This enables the encryption and decryption of a given file or directory using a pass-phrase. It also provides many different algorithms to accomplish this.
Install Mcrypt
Use the following commands to install Mcrypt on your system.
Default Algorithm (rijndael-128)
To use the default algorithm no additional options are required. In the example below, example.txt will be encrypted. After running the command below, a new file will be created called example.txt.nc with the .nc extension added to the end. Provide a pass-phrase when prompted, then confirm the pass-phrase.
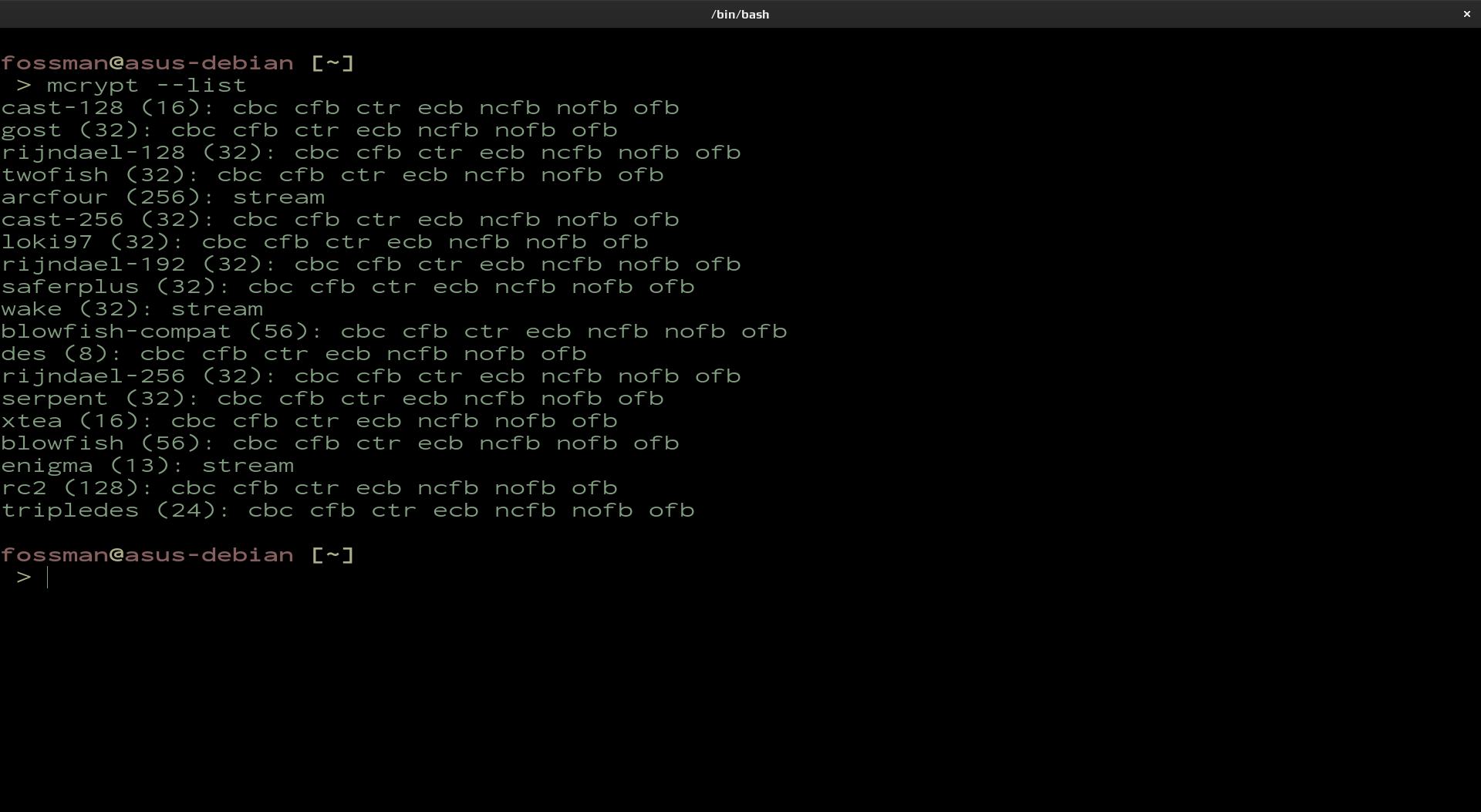
List Algorithms
If you would like to use a different algorithm, use the following command to display a full list.
Use Selected Algorithm
If you would like to use a different algorithm, use the -a option. In this example the blowfish algorithm will be used.
| mcrypt | name of the tool |
| -a blowfish | use the blowfish algorithm |
| example.txt | file to be encrypted |
Confirm algorithm used
To confirm the type of algorithm used, the file command can be used
Decrypt The File
To decrypt the file, use the following command with the -d option. Enter the pass-phrase when prompted.
Remove generated document
After decrypting the file, the decrypted version of the original file will be created. When you are done using the file, it can be deleted from the system leaving the encrypted version example.txt.nc using the following command.
02
GnuPG
GnuPG (GNU Privacy Guard) is a tool used for secure communication and data storage. It can be used to encrypt data and to create digital signatures. This section will cover how to encrypt directories or files using symmetric file encryption. Which will allow for the encryption of these files using a pass-phrase.
Install GPG
gnupg will most likely be installed on the system be default. If it is not already on your system, use the following commands to install gnupg.
fossworkx@linux-server:~$ sudo apt install gnupg
Default Algorithm (AES256)
To use the default algorithm, the -c can be used. After running the command below, a new file will be created called example.txt.gpg with the .gpg extension added to the end. --no-symkey-cache will prevent the system from caching the pass-phrase. Provide a pass-phrase when prompted, then confirm the pass-phrase.
| gpg | name of the tool |
| -c | use symmetric file encryption |
| --no-symkey-cache | do not cache pass-phrase |
| example.txt | file to be encrypted |
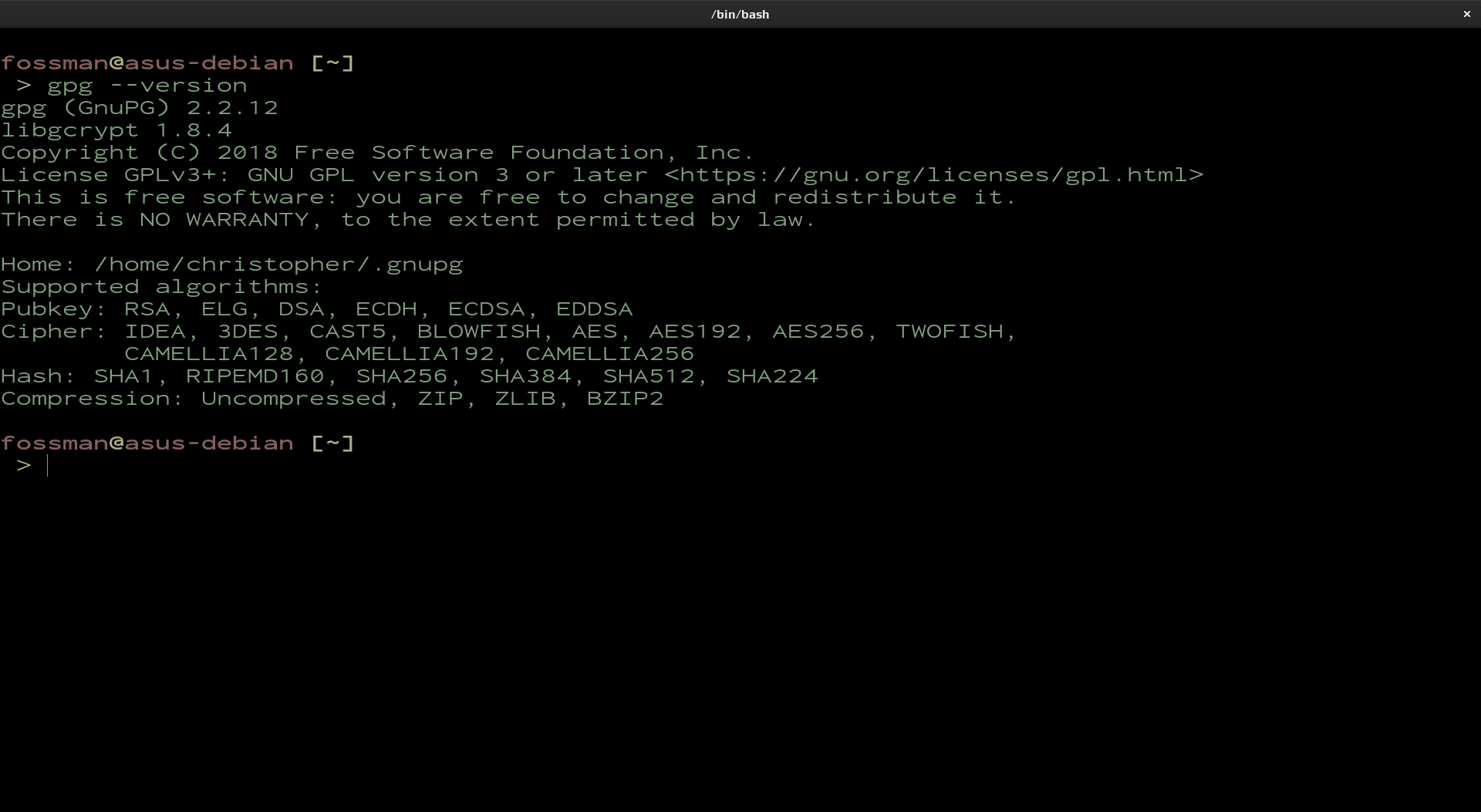
List Algorithms
If you would like to use a different algorithm, use the following command to display a full list.
Use Selected Algorithm
If you would like to use a different algorithm, use the --cipher-algo option. In this example the TWOFISH algorithm will be used. After the file is encrypted, the .gpg extension will be added to the end of the file.
| gpg | name of the tool |
| -c | use symmetric file encryption |
| --no-symkey-cache | do not cache pass-phrase |
| --cipher-algo TWOFISH | use the TWOFISH algorithm |
| example.txt | file to be encrypted |
Confirm algorithm used
To confirm the type of algorithm used, the file command can be used
Decrypt the file
To decrypt the file, use the following command with the -d option. Enter the pass-phrase when prompted.
| gpg | name of the tool |
| -d | decrypt the file |
| --no-symkey-cache | do not cache pass-phrase |
| example.txt.gpg | file to be decrypted |
After decrypting the file, the contents of the file will be returned to the screen. Due to the fact no additional files were created to view the file, there will be no additional files that will need to be removed for security reasons.